BoC set to leave interest rate unchanged amid rising inflation and US trade war

- The Bank of Canada (BoC) is seen keeping rates unchanged.
- The Canadian Dollar navigates the area of yearly highs vs. the US Dollar.
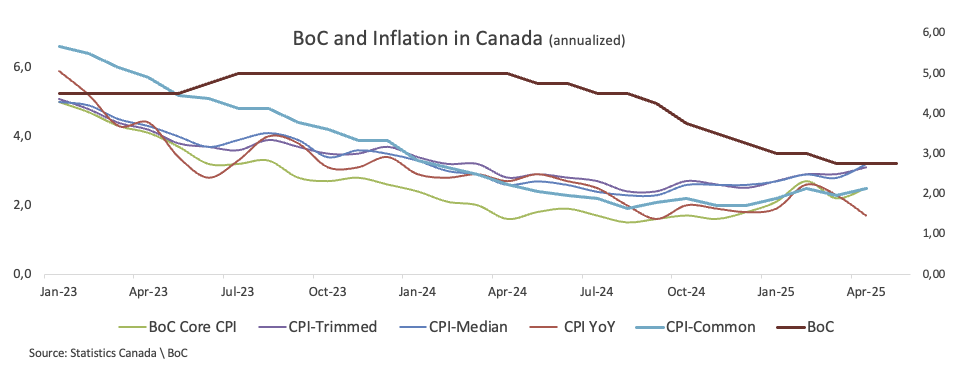
- Headline CPI in Canada drifted below the central bank’s target.
- Trade policies should prevail at Governor Macklem’s press conference.
Market analysts generally predict that the Bank of Canada (BoC) will keep its interest rate at 2.75% on Wednesday, adding to the pauses recorded at the March and April monetary policy meetings.
In the meantime, the Canadian Dollar (CAD) has been steadily appreciating since it fell to yearly lows in the 1.4400 zone against the US Dollar (USD). The Loonie is currently navigating the area of YTD highs in the proximity of the 1.3700 region.
Meanwhile, the focus has been on US President Donald Trump's trade policies, particularly those pertaining to tariffs, since he took office again in January. It is anticipated that this particular topic will take centre stage during the BoC event, influencing both Governor Tiff Macklem's remarks and media enquiries.
As growing global uncertainties, mostly caused by the White House's inconsistent stance on tariffs, compel a reexamination of trade policy, the Bank of Canada is planning to keep interest rates paused once again for June. Given this uncertainty, it is probable that the BoC's announcement and Governor Macklem's subsequent news conference this week will be cautious in tone.
Following the bank’s decision to keep rates unchanged on April 16, Governor Tiff Macklem underlined again the bank's symmetric approach to its inflation objective, expressing worry when inflation veers either over or below the 2% level. He stressed that the phrase "decisively", used in earlier exchanges, shouldn't be taken as a policy cue.
Regarding the general state of the economy, Macklem underlined the need for adaptation in view of continuous uncertainty, especially with regard to taxes. Once trade circumstances stabilise, the Bank may go back to a more defined base case projection.
Carolyn Rogers, senior deputy governor, dismissed recent market swings, saying it is too early to draw fundamental conclusions. She underlined that institutions are properly funded with some ability to withstand volatility and that Canadian financial markets remain orderly.
Regarding monetary policy, Macklem said that the Governing Council debated between maintaining rates constant or cutting 25 basis points. Rogers also mentioned several Council members who were really hopeful and not anticipating further inflationary pressure.
Previewing the BoC’s interest rate decision, analysts Taylor Schleich and Ethan Currie at the National Bank of Canada noted, "We expect the Bank of Canada to leave its policy rate unchanged at 2.75%... The labour market—which carries a lot of weight—is consistent with further rate relief, but the inflation picture right now isn’t giving the green light. There are also still key unknowns on trade impacts, inflation expectations and fiscal policy which further obscure the picture.”
When will the BoC release its monetary policy decision, and how could it affect USD/CAD?
The Bank of Canada will announce its policy decision on Wednesday at 13:45 GMT, with Governor Tiff Macklem holding a press conference at 14:30 GMT thereafter.
Market observers do not expect significant surprises; however, they anticipate that the central bank will maintain its emphasis on the effects of US tariffs on the Canadian economy. This perspective may also have repercussions for CAD fluctuations.
Senior Analyst Pablo Piovano from FXStreet highlighted that “USD/CAD has recently broken below its key 200-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 1.4020, subsequently opening the taps for extra weakness in the next few weeks.”
“USD/CAD has hit a fresh 2025 bottom at 1.3673 on June 2, exclusively following dynamics around the US Dollar. Once this level is cleared, extra losses could extend to the September 2024 low at 1.3418 reached on September 25,” Piovano added.
Piovano notes that “on the upside, the pair should encounter initial resistance at its May top of 1.4015 recorded on May 12 and May 13. This region of monthly peaks appears reinforced by the vicinity of the key 200-day SMA. If the pair manages to surpass the latter, it could embark on a potential visit to the next upside targets at the April high at 1.4414 set on April 1, ahead of the March top at 1.4542 recorded on March 4, and ultimately the 2025 peak at 1.4792 reached on February 3.”
“Currently, the Relative Strength Index (RSI) has dropped below the 40 level, suggesting further weakness remains in the pipeline. In addition, the ongoing bearish trend looks solid, as indicated by the Average Directional Index (ADX) around the 27 zone,” Piovano concludes.
Bank of Canada FAQs
What is the Bank of Canada and how does it influence the Canadian Dollar?
The Bank of Canada (BoC), based in Ottawa, is the institution that sets interest rates and manages monetary policy for Canada. It does so at eight scheduled meetings a year and ad hoc emergency meetings that are held as required. The BoC primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means keeping inflation at between 1-3%. Its main tool for achieving this is by raising or lowering interest rates. Relatively high interest rates will usually result in a stronger Canadian Dollar (CAD) and vice versa. Other tools used include quantitative easing and tightening.
What is Quantitative Easing (QE) and how does it affect the Canadian Dollar?
In extreme situations, the Bank of Canada can enact a policy tool called Quantitative Easing. QE is the process by which the BoC prints Canadian Dollars for the purpose of buying assets – usually government or corporate bonds – from financial institutions. QE usually results in a weaker CAD. QE is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the objective of price stability. The Bank of Canada used the measure during the Great Financial Crisis of 2009-11 when credit froze after banks lost faith in each other’s ability to repay debts.
What is Quantitative tightening (QT) and how does it affect the Canadian Dollar?
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse of QE. It is undertaken after QE when an economic recovery is underway and inflation starts rising. Whilst in QE the Bank of Canada purchases government and corporate bonds from financial institutions to provide them with liquidity, in QT the BoC stops buying more assets, and stops reinvesting the principal maturing on the bonds it already holds. It is usually positive (or bullish) for the Canadian Dollar.
Economic Indicator
BoC Interest Rate Decision
The Bank of Canada (BoC) announces its interest rate decision at the end of its eight scheduled meetings per year. If the BoC believes inflation will be above target (hawkish), it will raise interest rates in order to bring it down. This is bullish for the CAD since higher interest rates attract greater inflows of foreign capital. Likewise, if the BoC sees inflation falling below target (dovish) it will lower interest rates in order to give the Canadian economy a boost in the hope inflation will rise back up. This is bearish for CAD since it detracts from foreign capital flowing into the country.
Last release: Wed Apr 16, 2025 13:45
Frequency: Irregular
Actual: 2.75%
Consensus: 2.75%
Previous: 2.75%
Source: Bank of Canada







