AUD/JPY Price Forecast: Holds gains above 100.00, overbought RSI warrants caution for bulls

- AUD/JPY edges higher to near 100.05 in Wednesday’s early European session.
- The cross keeps the bullish view, but the overbought RSI condition might cap its upside.
- The key resistance level is seen at 101.56; the initial support level is located at 99.16.
The AUD/JPY cross extends its upside to around 100.05 during the early European session on Wednesday. The Japanese Yen (JPY) faces some selling pressure against the Australian Dollar (AUD) as traders assess the likely policy stance of Japan’s next Prime Minister, Sanae Takaichi.
Following Takaichi's victory, traders reduced bets that the Bank of Japan (BoJ) will hike interest rates this month. Takaichi indicated she wants the central bank to proceed cautiously on a rate hike and favors close communication between the central bank and the government. Money market traders are currently pricing in nearly a 26% odds that the BoJ will raise interest rates at its next policy meeting on October 30, down from around 60% before Takaichi's leadership victory, according to Bloomberg.
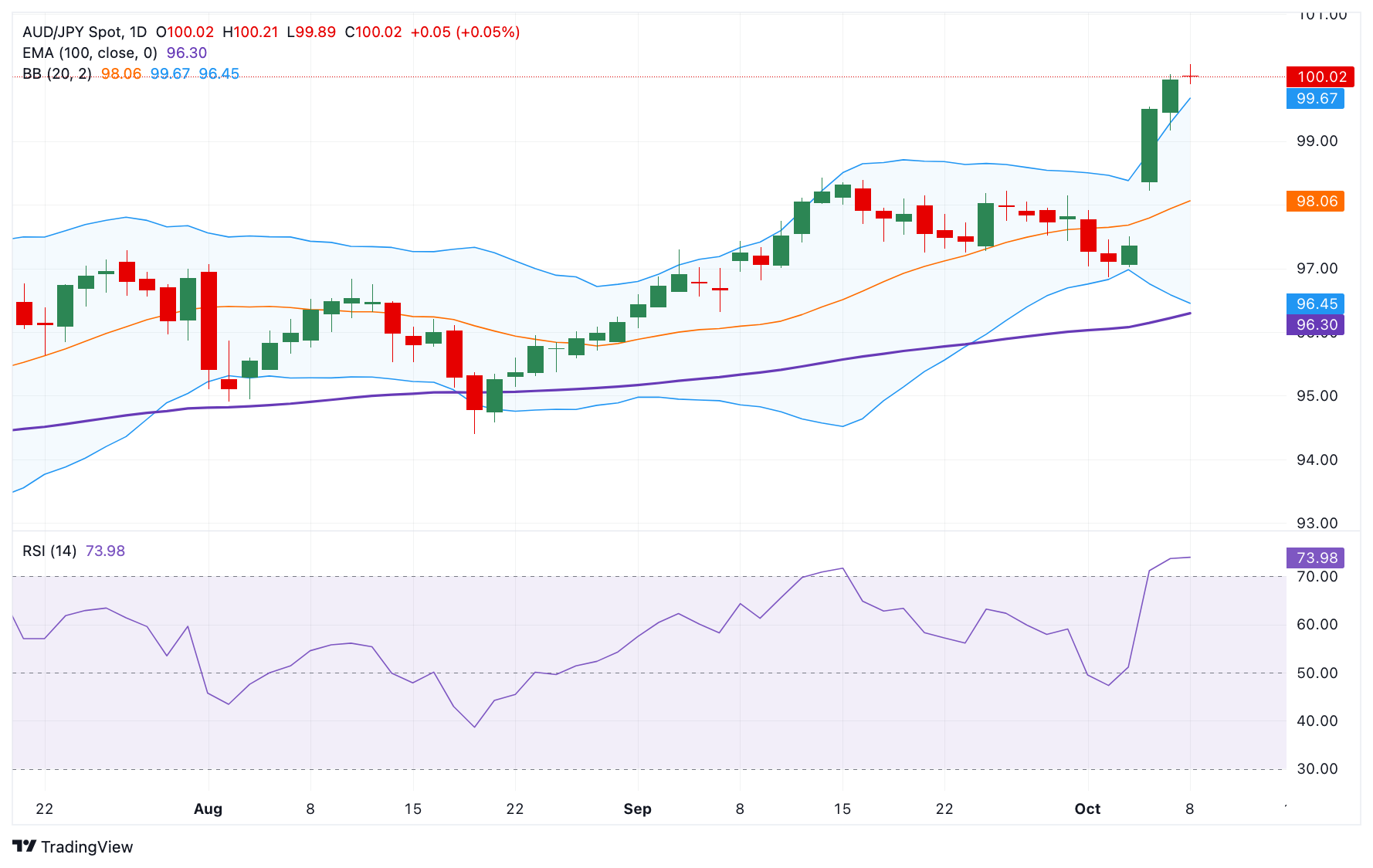
According to the daily chart, the positive view of AUD/JPY remains in play as the cross is well-supported above the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA). Nonetheless, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) stands above the midline near 74.25, indicating the overbought RSI condition. This suggests that further consolidation or a temporary sell-off cannot be ruled out before positioning for any near-term AUD/JPY appreciation.
On the bright side, the first upside barrier for the cross emerges at 101.56, the high of November 20, 2024. Further north, the next hurdle is seen at 102.30, the high of November 8, 2024. A decisive break above this level could pick up more momentum and aim for 103.48, the high of April 26, 2024.
On the other hand, the initial support level for AUD/JPY is located at 99.16, the low of October 7. Any follow-through selling below this level could expose 98.35, the high of September 15. The crucial contention level to watch is in the 96.45-96.30 zone, representing the 100-day EMA and the lower limit of the Bollinger Band.
AUD/JPY daily chart
Japanese Yen FAQs
The Japanese Yen (JPY) is one of the world’s most traded currencies. Its value is broadly determined by the performance of the Japanese economy, but more specifically by the Bank of Japan’s policy, the differential between Japanese and US bond yields, or risk sentiment among traders, among other factors.
One of the Bank of Japan’s mandates is currency control, so its moves are key for the Yen. The BoJ has directly intervened in currency markets sometimes, generally to lower the value of the Yen, although it refrains from doing it often due to political concerns of its main trading partners. The BoJ ultra-loose monetary policy between 2013 and 2024 caused the Yen to depreciate against its main currency peers due to an increasing policy divergence between the Bank of Japan and other main central banks. More recently, the gradually unwinding of this ultra-loose policy has given some support to the Yen.
Over the last decade, the BoJ’s stance of sticking to ultra-loose monetary policy has led to a widening policy divergence with other central banks, particularly with the US Federal Reserve. This supported a widening of the differential between the 10-year US and Japanese bonds, which favored the US Dollar against the Japanese Yen. The BoJ decision in 2024 to gradually abandon the ultra-loose policy, coupled with interest-rate cuts in other major central banks, is narrowing this differential.
The Japanese Yen is often seen as a safe-haven investment. This means that in times of market stress, investors are more likely to put their money in the Japanese currency due to its supposed reliability and stability. Turbulent times are likely to strengthen the Yen’s value against other currencies seen as more risky to invest in.







