Pound Sterling extends winning streak against US Dollar ahead of key UK-US data

- The Pound Sterling gains to near 1.3480 against the US Dollar as firm expectations of Fed rate cuts weigh on the Greenback.
- Fed Governor Bowman said she sees three interest rate cuts this year.
- Investors await the UK employment and the US CPI data on Tuesday.
The Pound Sterling (GBP) extends its winning streak for the fifth trading day against the US Dollar (USD) at the start of the week. The GBP/USD pair jumps to near 1.3480 due to the continued underperformance from the US Dollar, which is dragged by increasing expectations of interest-rate cuts by the Federal Reserve (Fed).
At the time of writing, the US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, trades 0.17% lower to near 98.00.
The US Dollar underperforms as traders have become increasingly confident that the Fed will reduce interest rates in the September policy meeting. According to the CME FedWatch tool, there is an 88% chance that the Fed will cut the federal funds rate by 25 basis points (bps) to the range of between 4.00% and 4.25%.
Fed members have started arguing in favor of unwinding monetary policy restrictiveness as labor market conditions are cooling down. Over the weekend, Fed Governor Michelle Bowman said at the Kansas Bankers Association signaled that the soft Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) report for July has increased her confidence of three interest rate cuts this year.
“With economic growth slowing this year and signs of a less dynamic labor market becoming clear, I see it as appropriate to begin gradually moving our moderately restrictive policy stance toward a neutral setting,” Bowman said.
Daily digest market movers: Pound Sterling starts the week on a positive note
- The Pound Sterling trades higher against its peers at the start of the week as traders have trimmed expectations supporting further interest rate cuts by the Bank of England (BoE) in the remainder of the year. According to a report from Reuters, investors trimmed their expectations for BoE rate cuts after Thursday’s announcements by the central bank and are not fully pricing in the next reduction until February’s meeting, compared with December previously.
- On Thursday, the United Kingdom (UK) reduced interest rates by 25 basis points (bps) to 4% and guided a “gradual and careful” monetary easing path.
- BoE Chief Economist Huw Pill said on Friday he doubts that the central bank could continue reducing interest rates at the current pace amid escalating consumer inflation expectations. Pill stated that the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is focused on inflation projections in the two-to-three-year horizon. "There’s still a little bit further downward to go with Bank Rate. I think the pace at which those downward moves perhaps go forward is a little bit less clear than the pace that we’ve seen over the last year," Pill said in an online presentation to businesses that take part in BoE surveys.
- Going forward, investors will focus on the UK labor market data for the three-months ending June, which is scheduled to be released on Tuesday. On the same day, investors will also focus on the US Consumer Price Index (CPI) data for July.
- Investors will pay close attention to the UK employment data to get cues about whether firms are still hesitant to add jobs due to an increase in their contribution to social security schemes. Economists expect the ILO Unemployment Rate to have remained steady at 4.7%. Average Earnings (Excluding and Including) bonuses are estimated to have grown moderately by 4.7% on year, compared to the prior reading of 5.0%.
- Meanwhile, the US headline and the core CPI – which excludes volatile food and energy prices, are expected to have grown at a faster pace of 2.8% and 3.0% on year, respectively.
Technical Analysis: Pound Sterling returns above 20-day EMA
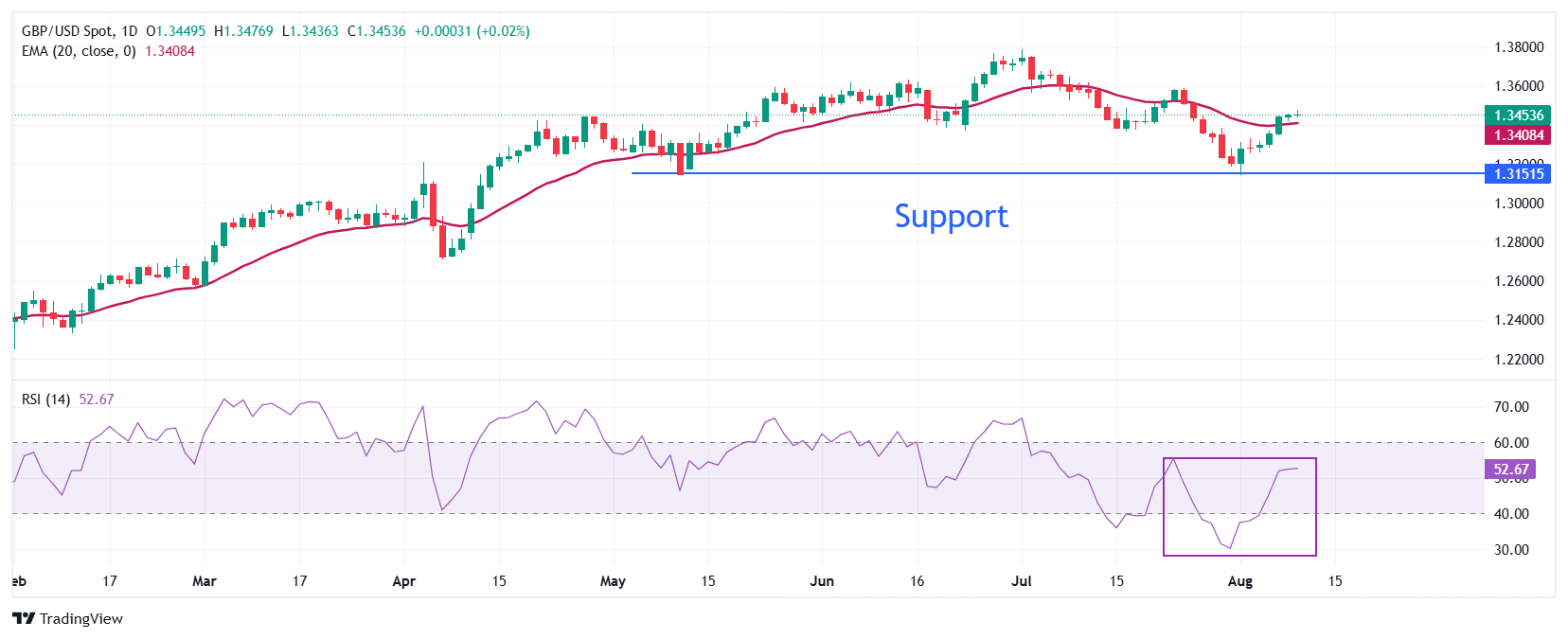
The Pound Sterling advances its week-long upside move to near 1.3480 against the US Dollar on Monday. The GBP/USD pair demonstrates strength as it has climbed back above the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which trades around 1.3408.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) bounces back above 50.00 after oscillating inside the 20.00-40.00 range in the past few trading sessions, suggesting an attempt for bullish reversal.
Looking down, the August 1 low of around 1.3140 will act as a key support zone. On the upside, the July 23 high near 1.3585 will act as a key barrier.
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.







