Gold slips as traders book profits despite increasing Fed dovish bets

- XAU/USD edges down 0.14% despite broad US Dollar weakness and falling yields.
- US Jobless Claims hit a four-year high, cementing 90% probability of Fed’s first 25 bps rate cut since December.
- Geopolitical risks persist after Poland downs Russian drones, bolstering safe-haven appeal even as traders lock gains.
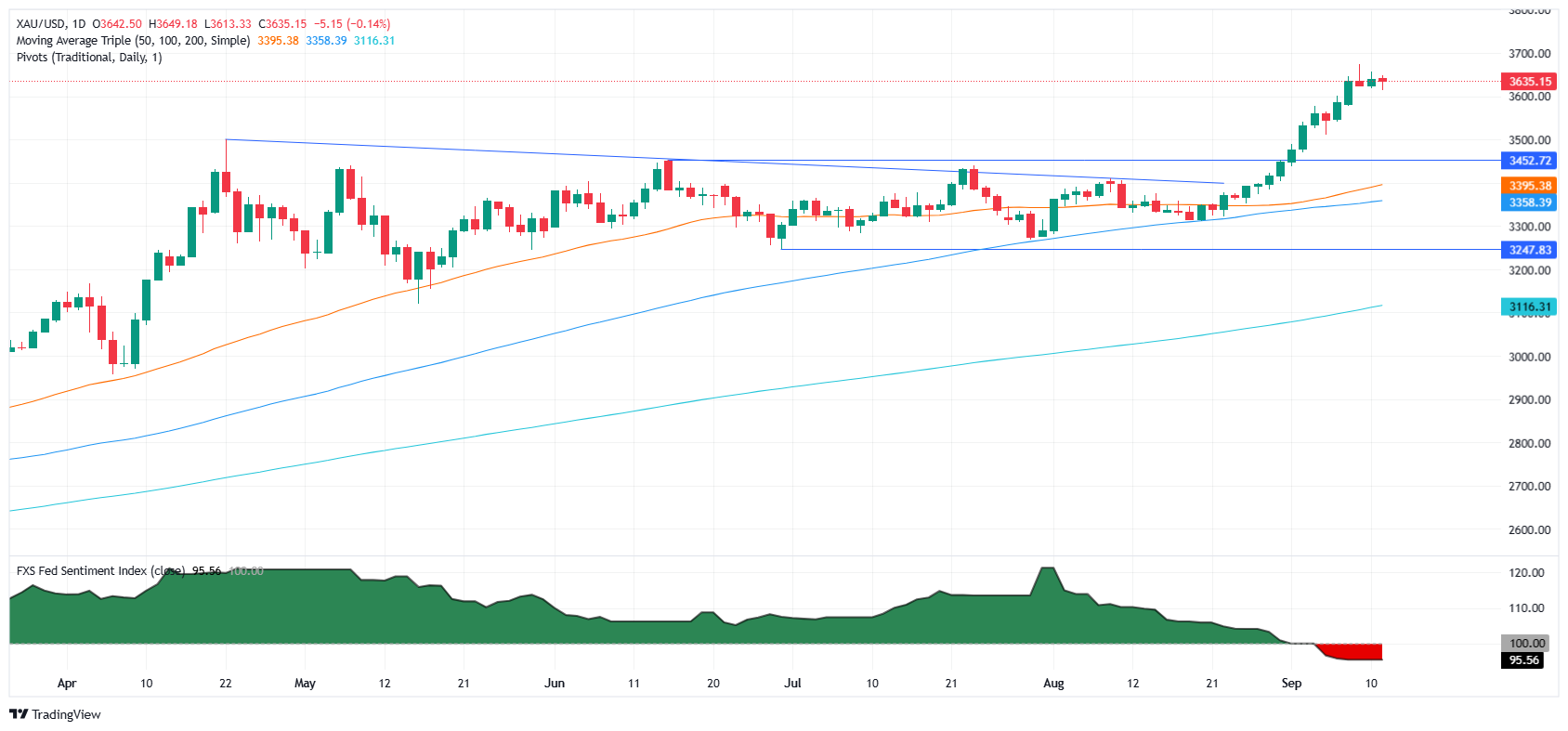
Gold price trimmed some of its earlier losses on Thursday, yet it remains negative in the day, down over 0.14% as the latest print of consumer inflation was aligned with estimates. Nevertheless, jobs data outweighed August’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) report as the number of Americans filing for unemployment benefits rose. XAU/USD trades at $3,635 after hitting a daily high of $3,649.
Bullion edges lower after soft CPI and higher Jobless Claims boost easing odds
The US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) revealed that inflation remained steady on the consumer side, with headline CPI standing below the 3% threshold. At the same time, the release of Initial Jobless Claims for the week ending September 6 rose to its highest level in almost four years. This cemented the case for a rate cut by the Federal Reserve (Fed) next week, the first one since December of last year.
Now with the CPI and the Producer Price Index (PPI) reports in the rearview mirror, money markets had priced in a 90% chance for a 25-basis points (bps) cut. Meanwhile, odds for a 50-bps cut are slim at 10%, according to the Prime Market Terminal interest rate probabilities tool
Even though this is bullish for Gold, it seems that traders are booking profits as the non-yielding metal has failed to gain traction, despite falling US Treasury yields and broad US Dollar weakness.
In the meantime, geopolitics would likely continue to boost Gold’s appeal after Poland attacked Russian drones over its airspace, which marks the first direct engagement on NATO countries after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Daily market movers: Gold edges up as US inflation ticks lower
- The US CPI in August increased from 2.7% to 2.9% YoY, as expected by estimates. Meanwhile, the Core CPI print remained steady at 3.1% YoY, aligned with projections and unchanged from July’s figures. Market’s reaction was muted, as Fed odds for rate cuts remained unchanged.
- Initial Jobless Claims for the week ending September 6 surged from 237K in the previous print to 263K, crushing forecasts of 235K.
- Following the Fed Chair Powell's speech at Jackson Hole, when he addressed that they would prioritize maximum employment over inflation, suggests that next week’s cut is fully priced in.
- Gold price rally is poised to continue rising, up so far 38.52% in year-to-date figure, as US President Donald Trump cut taxes, escalated the trade war and posed threats to the Fed’s independence.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the buck’s performance against a basket of six currencies, is down 0.22% at 97.59.
- US Treasury yields are falling, with the 10-year Treasury note down two and a half basis points (bps) to 4.019%. US real yields—calculated by subtracting inflation expectations from the nominal yield—have decreased nearly three basis points to 1.669% at the time of writing.
- The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) revised down its annual benchmark payrolls to -911K for the 12 months through March 2025, exceeding economists’ estimates of -682K, according to Bloomberg.
Technical outlook: Gold price hovers below $3,640
Gold price consolidates for the third straight day, after reaching an all-time high (ATH) of $3,674 on Tuesday. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) begins to show overbought conditions, capping Bullion’s uptrend.
If XAU/USD clears $3,650, expect a move towards the ATH ahead of $3,700. If surpassed, the next stop would be $3,750 ahead of $3,800. Conversely, if Gold tumbles below $3,600, the first support would be $3,550, followed by the April 22 high of $3,500.
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.







